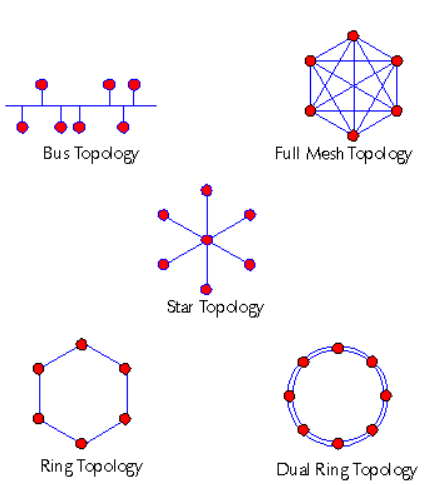
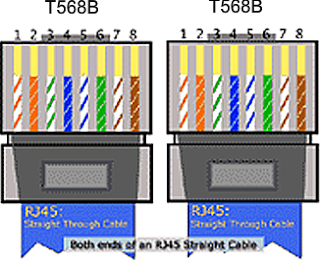
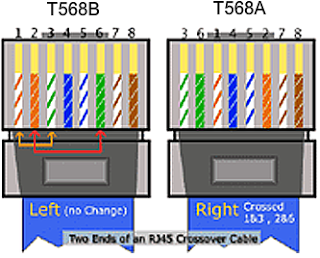
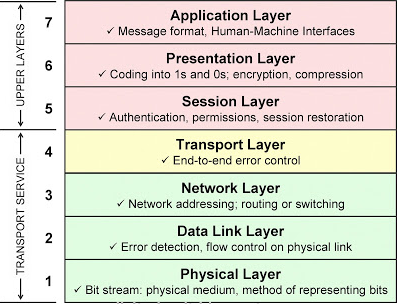
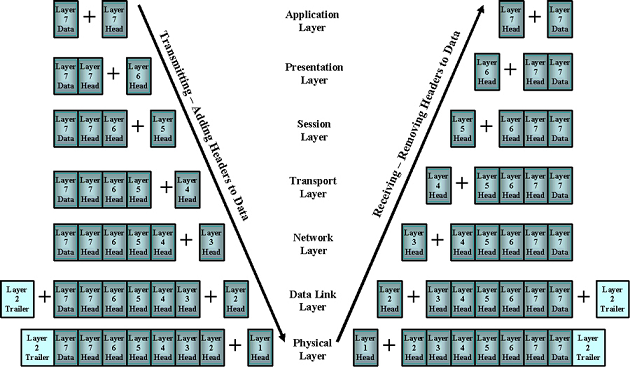
| Layer | Name | Function | Example protocols | Format | Network hardware |
|---|
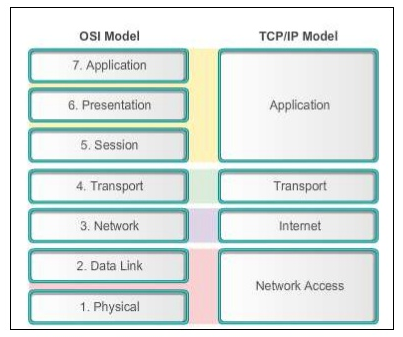
| 7 | Application | Interface between software applications and the network | Telnet, HTTP, FTP, SSH | Data | |
| 6 | Presentation | Handles encryption, message formatting, and compression | ASCII, JPEG, PNG | Data | |
| 5 | Session | Manages applications and establishes, maintains, and terminates user connections | Operating systems, scheduling | Data | |
| 4 | Transport | Provides reliable or best-effort data delivery with optional error and flow control | TCP, UDP | Segments | |
| 3 | Network | Provides logical end-to-end network addressing and routing | IP | Packets | Router |
| 2 | Data Link | Uses MAC addresses to access network devices. Provides error detection but no correction. | 802.3, 802.2, HDLC, FDDI, PPP, Frame relay | Frames | Switch, Bridge |
| 1 | Physical | Bit stream. Specifies voltage, wire speed, and cable pin outs | EAI/TIA, V.35 | Bits | Hub, Repeater, NIC |
| Layer | Name | Function | Example protocols | Format | Network hardware |
|---|
| 4 | Application | Provides network services to applications via services and protocols. Sockets and port numbers are used to differentiate the path and sessions on which applications operate. Message formatting and compression is provided. | Telnet, HTTP, FTP, SSH, JPG, Operating Systems Scheduling | Data | |
| 3 | Transport | Provides reliable or best-effort data delivery with optional error and flow control | TCP, UDP | Segments | |
| 2 | Internet | Provides logical end-to-end network addressing and routing. | IP | Packets | Router |
| 1 | Network Access | Encapsulates IP packets into frames for transmission. Maps IP addresses to physical hardware addresses (MAC addresses) and uses protocols for physical data transmission. | 802.3, 802.2, HDLC, FDDI, PPP, Frame Relay | Frames, Bits | Switch, Bridge, Hub, Repeater, NIC |